LOW BACK ACHE
Low back ache is a symptom not a disease.
Low back pain is very common symptom which affect 70% of population atleast once in lifetime.
Maximum incidence between 35-55 yrs age group
Usually a self limiting condition ,in about 10% may progress to chronicity
Types of low back ache
a) Within the spine (spondylogenic , neurogenic)
b) Outside the spine (viscerogenic, vascular, psychogenic)
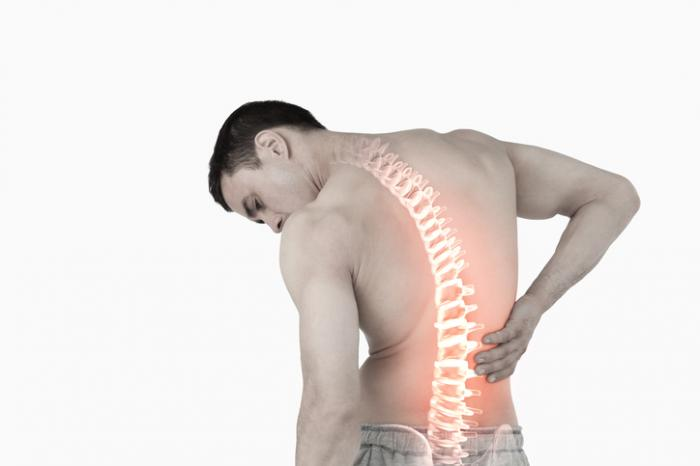
Low back ache can be with or without leg pain
a) low back ache without leg pain
1) ligamentous strain
2) muscle pain
3) facet pain
4) bony destruction
5) inflammation
b) low back ache with leg pain
1) radiculopathy
2) plexopathy
Alerts to onset of pain of pain in different age groups
a) Infancy and adolescence (infection and tumor)
b) Young and middle age groups (premature dic degeneration, spondyloarthropathies)
c) Older adults (disc degeneration)
d) Older age group ( metastasis, infection and osteoporotic fractures)
Aim of the doctor while examining pt with low back ache
a) To localize pain generator in the spine (facet or disc)
b) The neurological localization (myelopathy or radiculopathy)
c) The aetiological /pathological localization
Approach to pt with low back ache
a) History (pain onset , site of pain, nature , duration, intensity, radiation , aggravating and relieving factors, claudication,occupational history , other systems)
b) Examination (gait , inspection, palpation and movements with neurological examination. Must examine hip joints)
c) Investigations (blood workup , x rays , ct scan in trauma, mri scan)
Red flags in pt with low back ache (needs MRI scan for evaluation)
a) Cannot pass or control urine or stools
b) Reduced sensation or weakness in limbs or imbalance while walking
c) Sudden onset back ache with spinal tenderness
d) Trauma
e) Fever
Treatment depends upon the cause of the back ache
Treatment includes
a) Rest , activity modifications
b) Physiotherapy (ultrasound therapy , IFT, short wave diathermy, leg traction ) and core strengthening excercises
c) NSAIDS
d) Steroids
e) Local anaesthetic block
f) Surgery if still not improving with conservative management .

